Although isn’t a good practice push your changes to the repository without run automated tests and make sure that the code build, sometimes it happens. It may be a lack of attention or who know.
This could be even worst if you need to make some changes on the source code and you discover that someone else broke the build pushing untested code, what happens next is that you will spend some time figuring out what is wrong instead of produce something cool.
In this cases a Continuous Integration (CI) tool would help and give you confidence to commit and update your code regularly.
Today we are going to talk about Travis which is a CI Service that helps you keep your build running and your tests green!

Community
Its been a while since Travis was released, maybe 2011? To be honest I just get to know it this year and it has a huge base users.
Mostly, users come from open source projects hosted at Github. Travis is free to use for open source projects and there are some payed plans for private repositories, similar with what Github does.
Easy to get started
With a few clicks it is possible to monitor your personal or organization repositories.
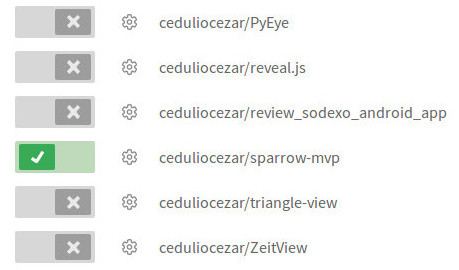
As you can see in the following image I’m currently just using Travis on one of mine.
In order to configure how Travis runs you should commit a file named .travis.yml on the root directory of your repository following the documentation.
Following there is an example of a yml file for an Andrroid project which is building the project, running tests and logging the result if something goes wrong.
How it works
After setup every time you commit or receive a pull request on a branch Travis CI will be notified that something is different and it will start the routine that you defined on .yml file.
If everything went is working as expected the build and tests will pass. If something goes wrong it will send you a notification by email telling you that something broke the build.
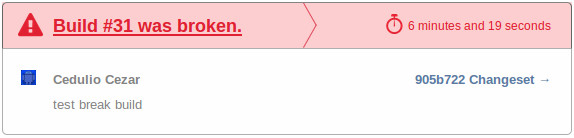
You will keep receiving this notifications until the build or tests were fixed and make everything green again.
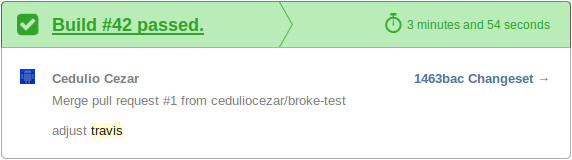
Android support
Though Travis documentation says that Android support is in beta, is possible to use and run even UI tests with Espresso and some emulators provided by Travis.
# Specify at least one system image,
# if you need to run emulator(s) during your tests
- sys-img-armeabi-v7a-android-19
- sys-img-x86-android-17
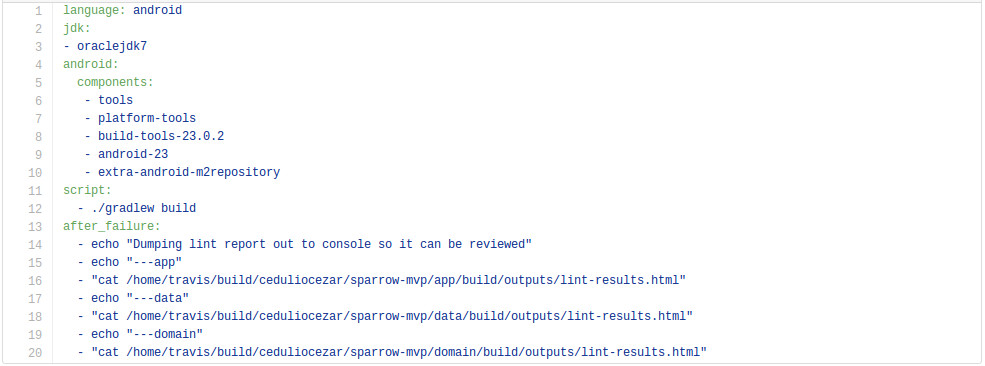
Logging Travis Results
After using Travis for a while you might find necessary to log the result if something goes wrong, because it won’t show unless you configure it.
Following the yml file that I’ve been using on an Android Project.
language: android
jdk:
- oraclejdk7
android:
components:
- tools
- platform-tools
- build-tools-23.0.2
- android-23
- extra-android-m2repository
script:
- ./gradlew build
after_failure:
- echo "Dumping lint report out to console so it can be reviewed"
- echo "---app"
- "cat /home/travis/build/ceduliocezar/sparrow-mvp/app/build/outputs/lint-results.html"
- echo "---data"
- "cat /home/travis/build/ceduliocezar/sparrow-mvp/data/build/outputs/lint-results.html"
- echo "---domain"
- "cat /home/travis/build/ceduliocezar/sparrow-mvp/domain/build/outputs/lint-results.html"
Conclusion
Travis CI is an awesome tool with a huge community of users, easy to use and free for open source projects. That you should take a look.
Credits
Header image “Parramatta River” by Tom Dawso is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.